Artificial intelligence (AI) has become part of everyday life. We chat with AI assistants, scroll through AI-curated feeds, and experiment with explicit AI generators that create images or text on demand. These tools are helpful, creative, and often fun to use. But they also raise important questions: why is data privacy important? How do AI companies handle personal information, and what can individuals do to stay in control?
This article looks at how AI interacts with data, what risks and concerns exist, what regulators are doing, and, most importantly, how to secure data in practical ways.
1. What does privacy mean in the context of AI?
Every time you use an AI tool, whether it’s a chatbot, an app or a generator, you contribute to artificial intelligence data collection. That might include the text you type, your voice commands or even images you upload. Much of this information is stored through AI data storage, and parts of it may be used to improve an AI data model. In some cases, data helps fuel explicit AI generators that create new content.
This cycle of collecting, storing, and training raises an essential question: why is data privacy important? The answer lies in control. Privacy allows you to decide how your information is used and for what purpose. Without it, you may not know whether your content supports advertising, algorithm training, or other uses you never expected.
And privacy is not only a digital matter. Using AI in public spaces carries a physical risk: someone nearby could glance at your screen. That is why AI data security goes hand in hand with practical steps such as using privacy screen filters or protective cases. Together, digital and physical measures create a stronger sense of control over personal information.
2. Real-World Examples: When AI Meets Privacy
Recent developments show how AI and privacy come together in practice:
- Meta’s training plans: In the Netherlands, regulators raised concerns when Meta announced it would use Facebook and Instagram posts to train AI. Unless users opted out, their public content could be built into an AI data model, making it part of the system permanently.
- OpenAI on teen privacy: OpenAI has emphasized that young people often share personal topics with AI. The company highlighted the need for strict protections and stronger AI data security to keep those conversations private.
- Research on interactivity: A Penn State study showed that playful, interactive AI apps make people less concerned about privacy. Users may share more information without realizing how much artificial intelligence data collection takes place in the background.
- Corporate best practices: Experts warn that without encryption and strong oversight, generative AI tools can expose sensitive information. Companies are encouraged to adopt “privacy by design” to secure data throughout AI data storage and model training.
These examples don’t suggest that AI is unsafe by definition, but they highlight the need for awareness about how personal data is handled.
3. The key privacy considerations
AI brings many benefits, but it also creates challenges for privacy. Some important points include:
- Data sharing happens easily: Conversations with chatbots often feel casual, but every word may be logged.
- Clarity is not always there: Users may not fully understand when content is used to train an AI data model.
- Storage policies vary: With long-term AI data storage, information can remain in systems much longer than expected.
- Information can leak: Under certain conditions, models may reveal data that was used in training.
- Sensitive groups need protection: Teenagers or people discussing personal matters require extra safeguards.
Recognizing these points helps users make more informed choices about the tools they use and the data they share.
4. Laws and Regulation in 2025
Governments and organizations are paying attention to AI privacy:
- European Union: Regulators have stressed that consent for data use must be explicit and easy to manage, especially in cases like Meta’s training plans.
- OpenAI: The company has introduced measures to limit staff access to user conversations and to improve safeguards for minors.
- Industry guidance: Security experts recommend embedding AI data security at every stage encryption, data minimization, and clear accountability for how data is used.
These steps do not remove every risk, but they show how oversight and industry standards are evolving to make artificial intelligence data collection more transparent and responsible.
5. How to protect yourself: Practical tips
Individuals can also take action. Here are some straightforward ways to strengthen privacy:
Digital practices
- Think before sharing: Avoid typing highly sensitive details into AI tools. Once added to an AI data model, it is unlikely to be removed.
- Check permissions: Review app settings for camera, microphone, and location access.
- Select platforms carefully: Choose services that clearly explain their policies on AI data storage and security.
- Use digital safeguards: Keep devices updated, enable strong passwords, and use two-factor authentication for added AI data security.
Physical practices
- Limit visual access: Use a privacy screen protector to prevent others from seeing your AI conversations in public.
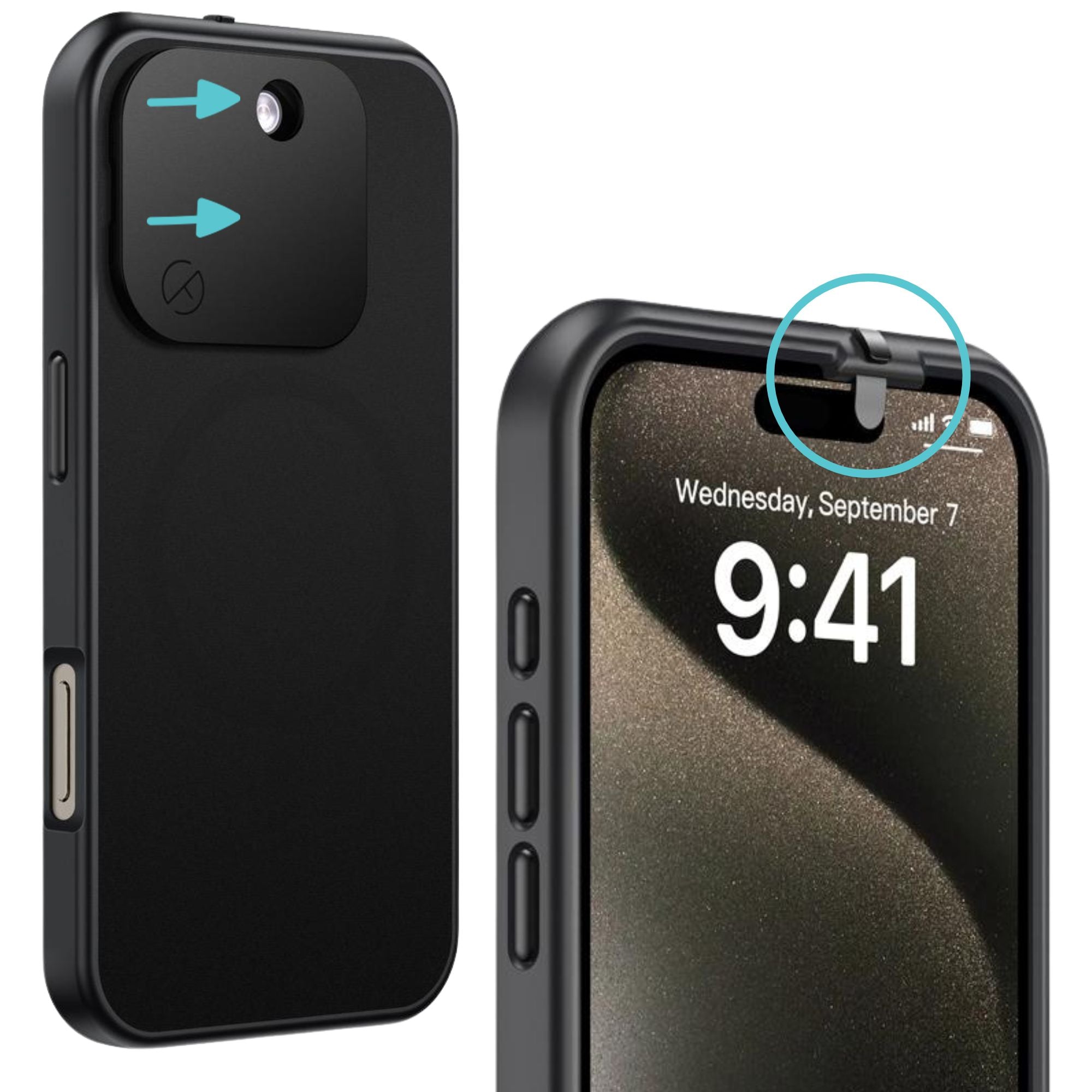
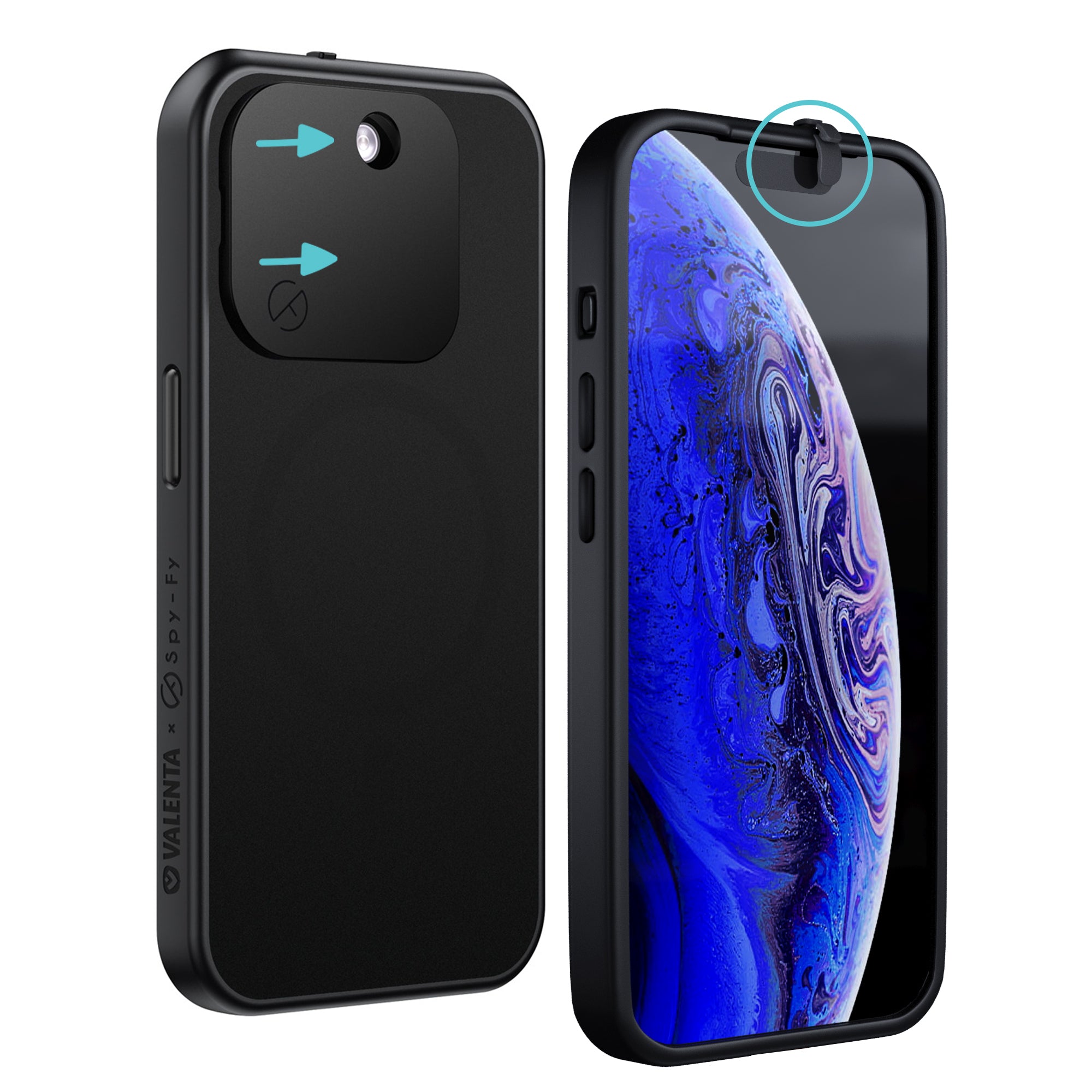
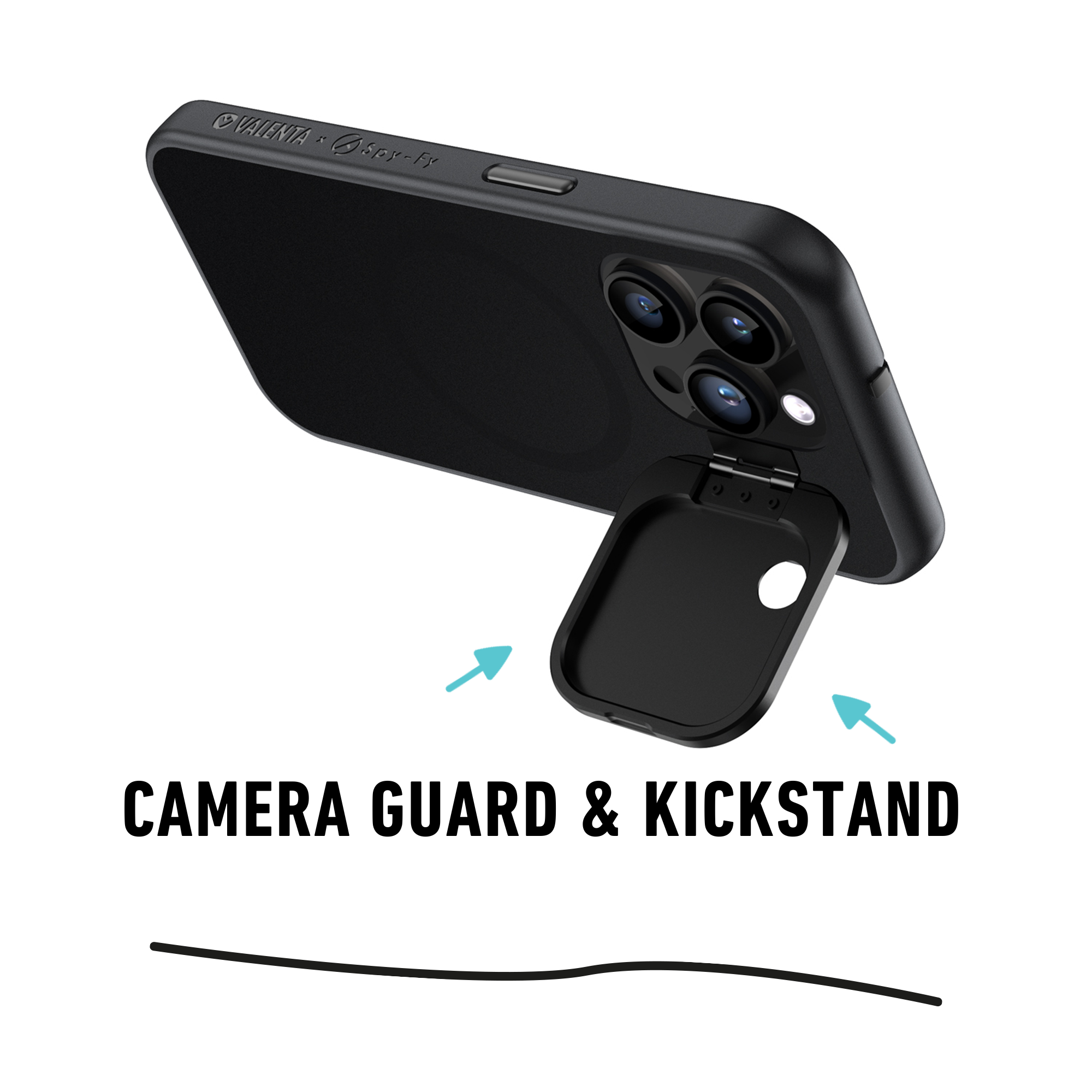
- Protect hardware: Phone cases or covers that block cameras and microphones can reduce the chance of unwanted access.
- Stay aware of surroundings: Treat AI interactions like private conversations, best held away from curious eyes.
Conclusion
AI makes life easier and more creative, but it also raises questions about privacy. Knowing why data privacy is important helps you stay in control of how your information is collected, stored, and used.
Awareness and small steps make a big difference. Alongside digital habits, physical tools help too. At Spy-Fy, we offer practical privacy products like phone cases that cover your camera, passport protectors, anti–juice jacking cables, and privacy screen filters so you can protect your data every day, both online and offline.